As companies have evolved over the past few years to adjust to the competitive and never-ending developing world, leaders of the organizations have known the importance of being Agile for enhancing their businesses. Agile Methodology has been widely accepted by many companies which were previously using traditional software methods. As Agile gives room for quick changes, adjusts to the market demand, and promotes creativity, many organizations now want to handle their operations using Agile methods. Scrum is one of the simplest frameworks of Agile Methods which is used by any company that begins to understand how Agile methodology works. Scrum is an iterative and incremental method of addressing complex problems and finding adaptive solutions. This means that Scrum finds solutions to problems in small intervals called Sprints where a Product Increment is built over a period. Scrum is lightweight, easy to understand, but difficult to master. The tools and techniques of Scrum may seem easy when any professional learns about them, but it may be challenging once the person applies them in real-life circumstances. In this article, we understand what Scrum framework is, Scrum’s accountabilities, events, rules which bind the framework, artifacts, etc.
What is Scrum?
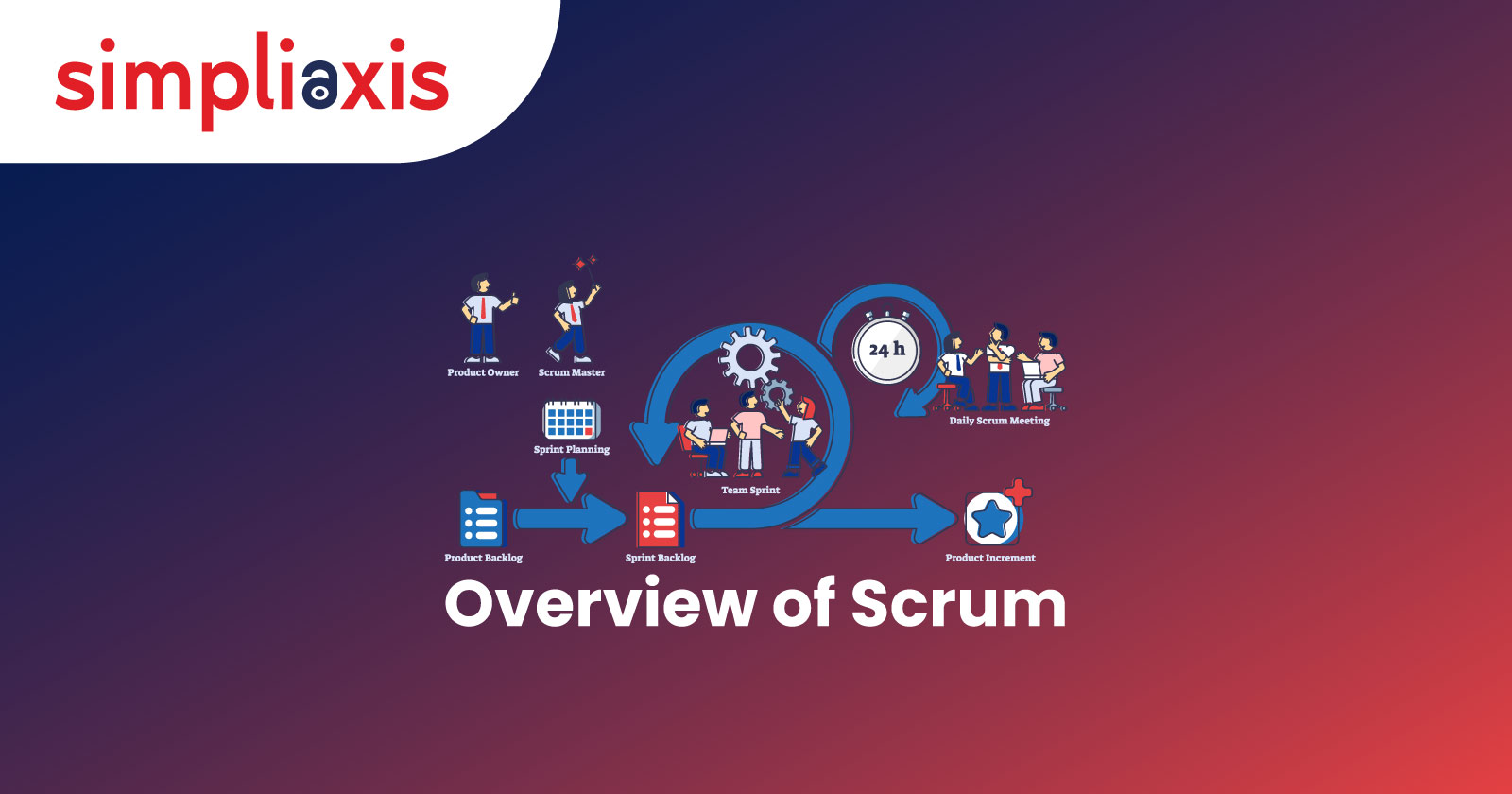
Scrum is a lightweight framework that is used to solve complex problems and find adaptive solutions which can generate value and help people, teams, and organizations. Scrum runs when a Scrum Master creates an environment for the teams to process the development, the Product Owner structures the complex problem that has to be converted into work, and the Scrum team converts the work into an increment of value. The stakeholders of the project along with the Scrum team members evaluate the Product Increment in a Sprint and the process is repeated till the product is developed. Sprint are periods which are about 2-4 weeks where the Scrum team decides to develop certain features of the product which is called Product Increment. Scrum does not give detailed instructions at the beginning of the project; it is purposefully incomplete and only the parts required to implement Scrum theory are defined.
What is Scrum Framework?
To simplify what the Scrum framework is, let us take an example of a product that is built using the Scrum framework. Unlike the traditional methods where all the steps of the development were planned in detail, Scrum believes in planning only for a few weeks and then reviewing work. The Scrum team begins by building a minimum viable product that contains the most important features of the product. Later on, the team works in time frames of maximum one month called Sprint where they begin to develop new features from the Product Backlog. These new features are selected based on the internal and external feedback received from the team members, stakeholders, and the users of the product. If a complex product is developed, multiple Scrum teams may work on the project. Scrum consists of various events where they plan and review the Product Increment. The process of developing the product in small intervals by anticipating the market trends and getting feedback is one of the main features of the Scrum framework.
Scrum Theory and Values
Lean thinking and empiricism are the main features on which Scrum was founded. Lean thinking cuts out the wastes and focuses on essentials, and empiricism focuses on the knowledge which is gained by experience and making observed decisions. The three pillars of Scrum are transparency, inspection, and adaptation. Transparency means that the progress of the work is visible to everyone and can make informed decisions based on the work progression. Inspection is the process of finding out whether the methods used for development are helping the project. It is used to detect undesirable variances and problems. Adaptation is the process of adjusting the process such that it meets the product goals and further deviation is minimized. Openness, respect, commitment, focus, courage, are the five important Scrum values that make the Scrum framework successful.
The Scrum Team
The unit of Scrum is a small team of people called the Scrum team which consists of one Product Owner, one Scrum Master, and the Developers. There are no subteams or hierarchies within the Scrum team as it is a cohesive unit of professionals who are focused on specific objectives at a particular time called the Product Goal. They are a self-managing, cross-functional team which means it consists of members who have all the skills which are required to create value at each Sprint. The typical size of the Scrum Team is typically 10 people or less. Scrum promotes accountability of the product to all the members and believes that everyone should own the product to develop it. This differs from the command and control way of development where all the accountability was of the Product Manager. When the size of the Scrum team becomes bigger, they are broken down into smaller teams that are all focused on the same project. Hence, they have the same Product Goal, Product Backlog, and Product Owner.
There are three primary accountabilities in Scrum- The Scrum Master, the Product Owner, and the Developers.
Scrum Master
The Scrum Master fosters an environment for the Scrum team members such that their concerns and ideas are heard and their development process becomes smooth. A few of their responsibilities are:
- Coaching the team members in cross-functionality and self-management and creating high-value increments which meet the definition of done.
- Removing the impediments to the Scrum team’s progress
- Conducting Scrum events and ensuring that all of them are productive and positive.
- Helping the Developers to understand the Product Goals and Product Backlog items.
- Helping the organization during the implementation of Scrum
- Coaching, leading, and training the organization in its Scrum adoption.
- Removing barriers between Scrum team and stakeholders.
Product Owner
The Product Owner is the person who represents the product and communicates with the customers and the Scrum team members. The PO orders the complex problem which is to be solved by the team and also owns the Product Backlog. A few of the roles and responsibilities of the PO are:
- Creating and communicating the Product Backlog items
- Arranging the items according to priority
- Ensuring that the Product Backlog is transparent and updated.
- Making the team understand the importance of the feature which is proposed to develop.
The Product Owner may delegate the work or can do it themselves. Either way, the PO remains accountable for its responsibilities.
Scrum Developers
They are the backbone of the Scrum team as they are committed to developing every aspect of the usable increment in each Sprint. Developers are always responsible for:
- Creating a Sprint and the Sprint Backlog
- Making sure the quality of the Product Increment is good.
- Progressing towards the Sprint Goal
- Holding themselves and each other accountable as good professionals.
The Developers give their opinions on the Product Backlog items and can also negotiate the work given during a Sprint by the Product Owner.
Scrum Events
Scrum Events are meetings that are held to structure and review the plans for the product. These events are designed such that the team does not need other meetings which are not defined in Scrum. The duration of the Scrum events is time-boxed and it is the responsibility of the Scrum Master to facilitate the meetings. The Scrum events are:
- Sprint Planning
- Sprint Review
- Sprint Retrospective
- Daily Scrum
- The Sprint
Sprint Planning takes place on the first day of the Sprint. The team members along with the Product Owner and the Scrum Master take part in this meeting. The Product Owner orders the Product Backlog items which have to be completed in the upcoming Sprint and explains the importance of each feature and how it will impact the product. The Scrum Team discusses and negotiates the work which they could complete within the Sprint. The team selects the items from the Product Backlog and places them in the Sprint Backlog. Every team has the same Product Backlog but has a different Sprint Backlog. Hence, as the name of the event suggests, the Sprint Planning meeting is primarily for planning the work for the upcoming Sprint.
Daily Scrum is a time-boxed event that occurs every day where the team members update everyone on how they are progressing in their work. It is completed in 15 minutes and is usually held in the same place and same time. The team members discuss what they have completed yesterday, what is their agenda today, and what are the impediments they are currently facing with their process. The Scrum Master notes the impediments and discusses the solutions after the meeting.
Sprint Review takes place on the last day of the Sprint where the stakeholders and Product Owner evaluates the work completed by the team in the Sprint. They give feedback on what all features can be improved and what new opportunities lie ahead for the product. The key stakeholders evaluate the progress of the product and may suggest the areas on which the team has to focus on based on the market trends.
The Sprint Retrospective is a meeting that is held after the Sprint Review where only the Scrum Team members attend without the stakeholders. In this meeting, the team discusses what they have lagged in the last Sprint and the methods they could improve in the next Sprint. Sprint Retrospectives help the team to understand their weak points and encourage them to improve on them. Also, this meeting can be used to build up morale by appreciating the team members for their achievements of the previous Sprint. Motivation and appreciation are the main features that are important for the team to achieve more in their project.
The Sprint is the heartbeat of Scrum where the ideas become valued in the form of the Product Increment. All of these meetings occur around the Sprint, which is a fixed-length period where the team has to create value. The Product Backlog is redefined during the Sprint, and the quality of the work does not decrease. Sprint helps the team to reach their Product Goals in steps and also gives them more ideas for the product along the way.
Scrum Artifacts
They represent work or values which are made to increase transparency. There are three Scrum Artifacts- Sprint Backlog, Product Backlog, and Increment. The Product Backlog is an ordered list of features which is needed for the product to improve. There is only one Product Backlog for a product from where all the work is derived. The Product Goal is the commitment for the Product Backlog. The Sprint Backlog is the list of features which is selected by the team which has to be completed during the Sprint. The Sprint Backlog consists of the Sprint Goal, the plan which delivers the Increment. The Increment is the step towards the Product Goal. After every Sprint, there are updates for the product which for example may be a bug fix or a new feature introduction. The commitment for the increment is the definition of done.
Simpliaxis is one of the leading professional certification training providers in the world offering multiple courses related to Agile methodologies. We offer numerous Agile related courses such as Certified ScrumMaster (CSM)® Certification Training, Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO)® Certification Training, Certified Scrum Developer (CSD) Certification Training, Agile and Scrum Training, PMI-ACP® Certification Training, Professional Scrum with Kanban™ (PSK) Training, Certified Scrum Professional® - Product Owner (CSP®-PO) Certification Training, Agile Sales Management Training, Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) Training and much more. Simpliaxis delivers training to both individuals and corporate groups through instructor-led classroom and online virtual sessions.
Conclusion
Scrum is an incremental and iterative framework that is used not only in information technology but also in many other industries. It is a method through which products could be built efficiently and effectively. Scrum helps the team to become Agile and be ready for changes that may affect the product. Any professional who is interested in Scrum and has an idea about Product development can become a Scrum Master or a Product Owner. To understand Scrum in detail, Scrum has introduced a Scrum guide that explains all of the aspects of Scrum from development to responsibilities.