What is the ITIL Framework?
TheITIL framework, which stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library, earns its primary recognition from businesses for its agility and efficiency. This is a set of best practices that supports and guides organizations in streamlining their IT infrastructure to meet business requirements.
The future of ITIL demonstrates a solid integration of AI, DevOps, and Cloud strategies to navigate the complicated roadmap of digital transformation.
Incepted in the year 1980, by the UK government's Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA), ITIL aids companies to gain optimal value so they can deliver exceptional results consistently.
What is IT Service Management (ITSM)?
The concept of ITSM also falls on similar lines as the ITIL framework. ITSM is a foundation that manages the IT technicalities and services of a company to align with its business objectives. A few other key aspects of ITSM are to consistently improve customer satisfaction and deliver growth.
Precisely, ITSM consists of:
- Design - Flawless IT Services
- Management - Manage the organization’s IT Structure
- Delivery - End-to-end IT-service delivery
- Assistance - 24*7 IT Support for clients
- Improvement - Day-to-day IT-related services
Companies that integrate ITSM in their operations rely on its strategic approach to manage IT applications and systems. This includes everything - from networking to storage options, data handling, hardware, and software components. Additionally, it also comprises safety, administration, and technical support.
The Four Components of ITIL 4:
ITIL 4 (Information Technology Infrastructure Library version 4) is a flexible service management framework recognized as the latest framework for managing IT-enabled services. In 2019, the ITIL model saw a revamp to align with the evolving digital transformation in the Information and Technology sector.
As we know, ITIL 4 is today the most popular management practice framework for IT management and digital services; we must also know the popular components of ITIL.
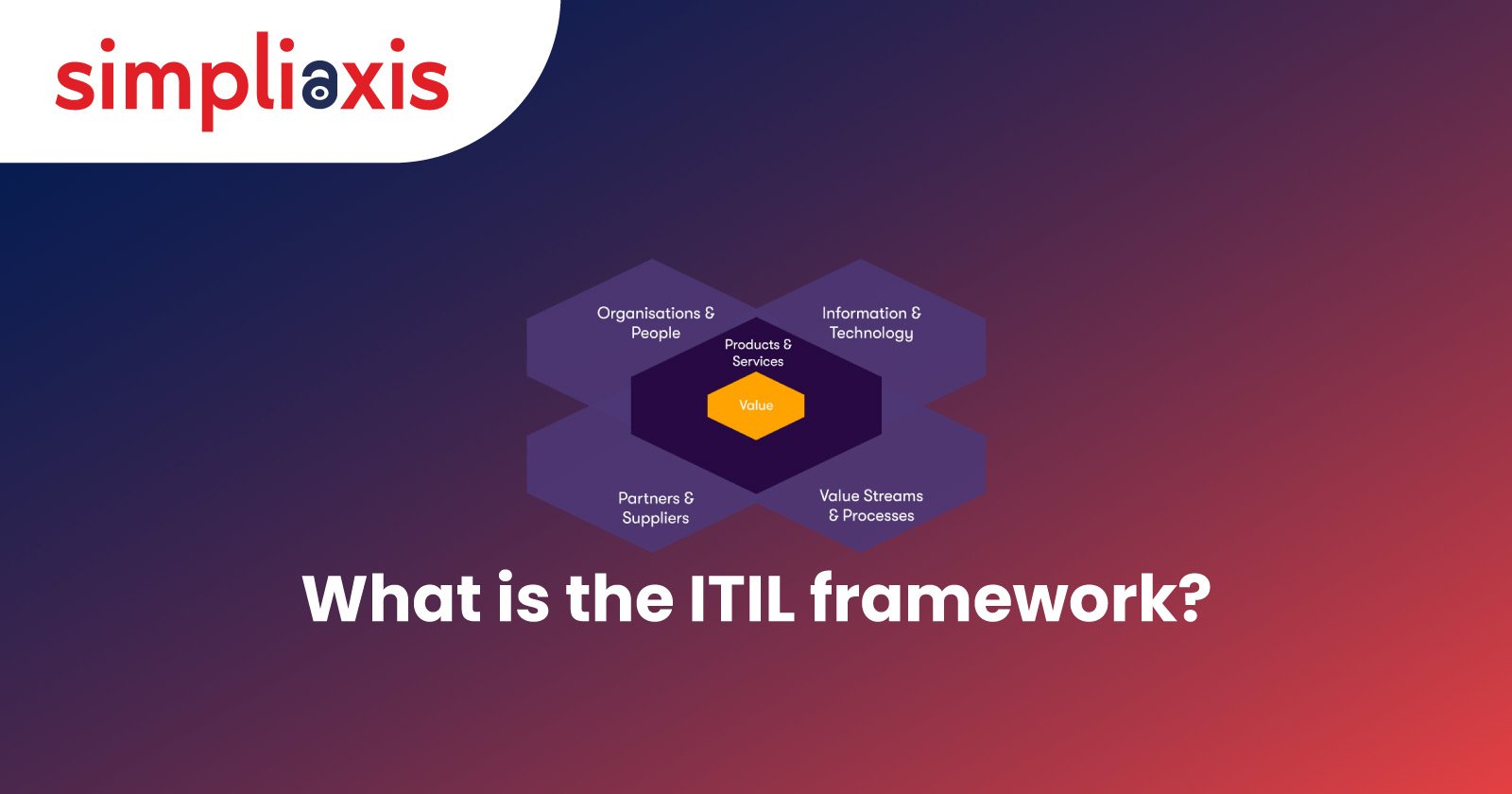
The four dimensions of ITIL 4 comprise:
1. Organizations and People - This dimension prioritizes the human resource department, the entire workplace, the workplace culture, the skills, and the organizational structure. Leadership, management, collaboration, and vision are the core ideas behind this aspect.
2. Information and Technology - As the term clearly defines, information and technology form the core component of ITIL 4, which offers IT assistance and support to the organization. Being an umbrella term, it encompasses everything - from Information Handling, Communications, Knowledge Base, Technology, and Cyber Security Management.
3. Partners and Suppliers - Corporate relationships rely on agreements and deliverables more than the day-to-day workings. The partners, suppliers, creators, and collaborators are integral parts of this dimension and contribute to the organization's welfare and success.
4. Value Streams and Processes - This segment of service management relies on synchronization between ideas and execution by producing value to its customers and clients with the effective use of its resources. It prioritizes creating value through products and services.
Understanding the Service Value Chain
The service value chain is a concept in the ITIL 4 framework that enables any organization or company to deliver products and services seamlessly by leveraging technology to its best advantage. It is an element in the Service Value System that promotes the holistic growth of organizations, along with creating value.
Being an integral part of the ITIL 4 service value system, this dynamic model creates and delivers value services to its customers. It consists of six interconnected key activities, namely:
- Plan
- Improve
- Engage
- Design and Transition
- Obtain
- Deliver
- Support
What are the ITIL Guiding Principles?
The term - Guiding Principles or ITIL Guiding Principles refers to the guidelines or principles (or recommendations) that companies or organizations follow when they set long-term goals using the ITIL framework.
These principles help create value for organizations with their client-centric and collaborative approach.
The 7 guiding principles are:
- Governance
- Value-centricity
- Continual Improvement
- Collaboration and Visibility Promotion
- Holistic Work Practices
- Ease and Viability
- Optimization and Automation
7 Top ITIL Best Practices to Enhance the End-User Experience
The ITIL Lifecycle
The ITIL Service Lifecycle is a framework that outlines the processes that are necessary to manage the entire life-cycle of products and services, required to deliver high-quality IT services from their inception till their closure or completion. It follows best practices that align with the business needs and contribute to its growth.
Dig deep to know what the 5 stages of ITIL are:
- Service Strategy - The strategies that a company designs to achieve a goal and address customer needs.
- Service Design - A stage that prioritizes new ideas for enhanced IT operations, aligning with the company's objectives.
- Service Transition - A move that involves any transition (including the addition or modification of an IT service).
- Service Operation - An integral stage in the ITIL Lifecycle that manages the day-to-day IT services in an organization to maintain timely deliverables and business operations.
- Continual Service Improvement - A practice in ITIL 4 is an ongoing phenomenon that aligns IT services with evolving business needs by referring to previous business records, to track successes and failures, for future improvements.
The ITIL 4 Practices and Processes
ITIL 4 comprises 34 practices, further broadly classified into 4 groups. Specifically, this framework does not refer to any particular processes but only recommends the following 34 practices and a Service Value System to offer value.
ITIL 4 Management Practices (Processes) | ||
|---|---|---|
| General Management Practices | Service Management Practices | Technical Management Practices |
| Strategy management | Business analysis | IT asset management |
| Portfolio management | Service catalogue management | Infrastructure and platform management |
| Architecture management | Service design | Software development and management |
| Service financial management | Service level management | |
| Workforce and talent management | Availability management | |
| Continual improvement | Capacity and performance management | |
| Measurement and reporting | Service continuity management | |
| Risk management | Monitoring and event management | |
| Information security management | Service desk | |
| Knowledge management | Incident management | |
| Organizational change management | Service request management | |
| Project management | Problem management | |
| Relationship management | Release management | |
| Supplier management | Change enablement | |
| Service validation and testing | ||
| Service configuration management | ||
| IT asset management | ||
ITIL Benefits and Business Value - How ITIL Helps Businesses to Build Business Value?
The ITIL 4 framework is exponentially beneficial for companies across all segments. It not only enhances service value efficiency but also brings collaborators together to brainstorm and ideate valuable output for customers.
There are both physical (tangible) and non-tangible (immaterial) benefits of ITIL that companies can experience with ITIL.
The top advantages of using the ITIL Framework for Business Value include:
- Cost-effectiveness - The ITIL framework helps optimize IT processes, thereby reducing expenses.
- Better Service Quality - With the right implementation of the standard procedures, ITIL helps in timely deliverables.
- Strategic Goal Alignment - By setting up clear, synchronized processes, ITIL helps in the timely attainment of business goals.
- Increased Productivity - With enhanced communication, appropriate resource allocation, and boosting consistent growth, ITIL helps boost productivity.
- Improved Decision Making - ITIL promotes decision-making significantly with enhanced coordination between teams and better choices.
- Customer Delight - Its approach towards exceptional service delivery for its clients helps establish a solid client base in every business.
The Real-World Impact of the ITIL Framework
As we know, companies have used the ITIL framework in their operations for ages; we must also know how it impacts the real world. Although there have been several new developments in this sphere, the everlasting influence, including both pros and cons, is worth taking into account.
Some of the notable advantages of the ITIL Framework include:
- A proactive, process-centric approach
- A reliable problem resolution setup
- Extraordinary IT support desk
- Validated service commitment
- Minimal disruption in operations
- Well-established communication channel
- Top-quality customer service
- Optimal use of resources
- Cost-effective course of action
- Challenges of the ITIL Framework
- Extensive, long-term proposal
- Capital-intensive set-up
- Potentially complicated process
- Inapt for modern-day needs
- Poor implementation
- Less beneficial for small companies
How ITIL Supports IT Governance and Risk Management?
While most companies and corporate heads rely on the ITIL Framework to navigate the IT complexities of the business, only a few actually comprehend its real-time benefit. ITIL is considered the most reliable and resourceful framework in the IT industry, ever since its inception. It defines all the right ways in which the IT segment (sector) governs businesses and helps in risk management.
To answer the question above, here are a few things to consider when it comes to ITIL and IT governance:
- The ITIL framework is closely related to IT handling and risk management, so it assists companies with seamless IT procedures, timely deliverables, consistent improvement, and accountability.
ITIL boosts service management, thereby creating transparency between IT functions, services, and business processes.
The framework further promotes the growth of individuals and the company by curating profile-centric responsibilities for the teams. - Continual supervision and optimization of IT services help track the performance of the team members involved.
Support IT investments to promote business strategies.
Similarly, the ITIL Framework also boosts risk management measures of companies by manifold. Take note of the following points to know how the ITIL framework works to minimize and mitigate your business risk.
- Its design is such that it identifies risks in any dynamic IT setting.
- Helps to avoid IT disruptions at any point in time.
- Guides about problems and helps discover new ways to minimize similar scenarios in the future.
- Improves compliance with consistent documentation and process.
Implementing ITIL along with the Steps
People who pursue the ITIL certification course or appear for the ITIL foundation examinationqualify to incorporate their ITIL knowledge in their workspace. But, for those who worry about how to put ITIL into practice? - Here is a more comprehensive take on its implementation we have defined through the steps discussed further in this post:
But before we delve into that, we must know why companies rely on the ITIL framework. Well, it is not only to streamline their operations but to work out a transparent process to manage IT commitments.
This also contributes to increased efficiency, minimized downtime, and enhanced orientation with major business objectives.
Steps to execute for utilizing ITIL for business success:
- Attend the ITIL foundation training, rather than earning only a certification. Try to understand the course in detail - from the practices to the concepts.
- Aim to do more than just earn a certification for the course. Learn more to strengthen your profile for a greater scope.
- Focus on how you can implement the qualifications earned into your business. Understand how ITIL contributes to creating quality services and business value.
- Go back to the ITIL study materials in case of confusion or lack of clarity.
- Monitor the performance of your business and work on the areas of improvement as needed.
- Prioritize customer satisfaction with consistent feedback, optimized resources, and improved services.
Is the ITIL Certification Worth it?
Any professional certification degree is valuable, provided it makes you a more informed individual and encourages you to do better, both personally and professionally. So, when it comes to earning an ITIL certification, individuals can find countless career options worth choosing from once they complete the course.
Furthermore, the ITIL certification benefits also open up high-paying job opportunities, create valuable positions, and build efficiency for the individual. Universities across the globe consider ITIL an integral qualification as it goes beyond a single career option or industry, and sets a solid foundation for growth.
What is the Configuration Management Database (CMDB)?
The CMDB is an ITIL term that companies use to store all the hardware and software-related information of their assets. One can consider this to be a consolidated repository that safely compiles and retains the details about all the configuration items.
This includes any component of the IT infrastructure, including the hardware, software (or everything that links them together), other than documentation, email services, the people involved, etc.
Here, try to understand a straightforward example of the CMDB via a company that has a streamlined IT infrastructure. For instance, in a firm where there are well-set server structures, automation is a priority for continual configuration and behavior; there will be consistent, scalable, and reliable growth.
Incident Management vs Problem Management
Incident Management and Problem Management are two different ITSM processes that come together to manage IT services and minimize disruptions in the process. While the former primarily focuses on re-establishing services post an interference in the system, the latter detects issues and reduces the chances of similar happenings.
We have further highlighted the major differences between the two in the table below:
Parameters | Incident Management | Problem Management |
Objective(Focus) | To recover normal service operations at the earliest, once an issue is detected. | To mitigate new issues by identifying the root cause and minimizing its impact on the business operations. |
Process | The error or incident is first identified, then documented, followed by its classification. | Involves early detection, logging, categorizing, and systematizing. Followed by finding a permanent fix and timely documentation. |
Priority | Tasks are addressed based on requirement and urgency. | To prevent the recurrence of tasks by identifying the root problems. |
Response Time | The duration during which an incident is reported and then acknowledged by the response team. | No fixed response time, as it is defined by SLAs (based on the magnitude of problems) |
Documentation | Documentation includes templates, policies, reports, and processes that help address unexpected disruptions in the system. | Involves the detection of potential problems and their diagnosis, followed by resolution, after everything is documented. |
Relationship | Spontaneous to any ongoing situation and primarily deals with the reason behind the disruption. | Proactive in problem management to prevent future issues. |
Resolution System | Often works out a short-term solution to resolve problems and restore services speedily. | Focuses on permanent resolution by eliminating the root cause. |
Read More: Four dimensions of ITIL service management
ITIL Foundation Editions
The ITIL Foundation Edition, also known as the ITIL 4 Foundation, is a beginner-level certification that guides applicants to the ITIL Framework, which manages the IT needs of a business.
Precisely, this certification prioritizes ITIL implementation and practice at the workplace. Companies today, across several industries and segments, rely on this framework to synchronize and support IT components.
Read More: ITIL Implementation Challenge
ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification
The term “ITIL 4 Managing Professional Certification” is the latest IT service management (ITSM) designation that extends extensive, practical knowledge about managing IT-authorized services. It further introduces individuals to the core concepts of team handling, delegation, responsibilities, and workflows.
A minimum criterion to qualify for ITIL Managing Professional Certification is the ITIL 4 Foundation certification, followed by the qualifying examinations for the 4 expert modules.
ITIL 4 Strategic Leader Certification
This one is also a professional designation for individuals looking for solutions to align digital strategies with IT protocols to achieve business milestones.
ITIL 4 Master Certification
It is the highest level of ITIL certification, which prioritizes proficiency in the ITIL framework through hands-on application and experience.
ITIL 4 in AI-Driven Service Management
As the name suggests, this encompasses the use of AI to streamline, process, and optimize ITSM operations for enhanced user experience, on-time deliverables, and a reduction in costs. This process integrates the use of ML (Machine Learning) and NLP (Natural Language Processing) into core ITIL practices.
Read More: Is ITIL Certification in Demand?
The Role of AI in ITIL-Centric Operations
There is no denying the fact that IT sees a significant influence of Artificial Intelligence in its operations. Today, every new business model works on automation and smart workflow systems, and the credit goes to all the AI-driven workplace solutions that give companies an edge over their competitors.
Whether it is to automate tasks, manage multiple teams, collect data, create, maintain, and update IT collaborations, or track complex records, AI can significantly assist in everything that revolves around technology management and industry transformation.
Read More: What do you mean by Generative AI?
Scalability by Company Size
The term “scalability” refers to a process that efficiently handles the surging demand for work without letting go of the core business principles, standard of delivery, and stability.
Every company aims to be scalable by bringing in place its exceptionally trained and dedicated workforce, systematized procedures, automating operations, and keeping the expenses in check.
ITIL Experts and Resources
Companies often hire certified IT service management professionals who have in-depth expertise and practical knowledge of the ITIL framework. The reason for this is that they bring along their reliable mastery, precision, and years of practice to the job.
This is the most valuable resource for companies, other than the virtual resources (publications, training courses, webinars, etc.) available on the internet. Apart from this, the ITIL experts pay attention to the countless other easily-accessible resources like study materials and guides that support companies with their valuable content (policies, protocols, and practices).
Also Read: How to Become a Certified ITIL Expert?
The concept of ITIL is crucial to every business and enterprise, and plays an important role in rationalizing and structuring IT services. With its deep-rooted principles and policies, it not only drives customer satisfaction but also business success and growth.